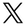A new process developed by the Fraunhofer Institute makes it possible to make paper water-repellent using plant-based substances. Plasma polymerisation could replace plastic packaging in the future and improve the recyclability of paper.
In order to Fully utilising the potential of paper as a material, In order to improve recycling options, replace plastic packaging and open up new fields of application, the durability, resistance and quality of paper products must be improved. Researchers at the Fraunhofer IST in co-operation with the Technical University of Darmstadt and the Thünen Institute of Wood Research in the BioPlas4Paper project. To Homogeneous, moisture-repellent layers on paper the project partners rely on plant substances such as oregano or chia oil and extracts obtained from bark material. These plant substances are characterised by their antibacterial effect, among other things.
„We use previously unutilised plant substances with a high proportion of unsaturated fatty acids to make paper hydrophobic, i.e. water-repellent. To do this, we use atmospheric pressure plasma technology, in which gas is excited by means of high voltage under ambient pressure in such a way that a plasma, i.e. a mixture of particles consisting of ions, free electrons and usually also neutral atoms or molecules, ignites. A discharge occurs between the electrodes.“
Martin Bellmann, scientist at the Fraunhofer IST in Braunschweig
The plant substances are converted into an aerosol by the addition of nitrogen and introduced into the plasma as vapour-like organic precursor compounds in order to form polymer networks. Experts refer to this process, in which the precursor compounds are activated by a plasma, as Plasma polymerisation. The micrometre-sized particles combine with each other to form plasma polymers, the tiny However, droplets also cross-link with the paper and lay down on the surface. onto the rough paper substrate, penetrating deep into the pores and fibres of the surface. „The plant molecules only become reactive and cross-link to form polymers when the plasma is applied,“ explains the researcher.
The plasma is generated using a plasma source by ionising gas between two rotationally symmetrical electrodes to which high voltage is applied. New are the geometric arrangement of the electrodes, and the way in which the aerosol is introduced. and how the plasma is ignited. The combination of these measures results in an innovative concept that the researchers developed specifically for the project, so that the effects of the ambient air are minimised under atmospheric pressure, even at higher coating speeds, and the results are consistent and reproducible.
„Due to the roughness of the paper surface, the ambient air swirls at high processing speeds, which changes the plasma properties. We can avoid these harmful influences with our concept.“
Martin Bellmann

The plasma source is brought close to the paper surface and completely displaces the ambient air. In order not to impair the paper itself, the bio-based precursor molecules and the properties of the plasma polymers produced, the researchers are working with Plasma temperatures of around 70 degrees.
In numerous tests with a wide range of vegetable oils and extractives, the researchers were able to prove that biobased substances can be reproducibly and homogeneously separated using plasma. Very good hydrophobic layers could be created with olive and chia oil, for example. can be achieved. Depending on the precursor compounds used and the coating parameters, the researchers can influence and optimise the layers. The aim is to equip paper as a material for ever more demanding utilisation scenarios and thus replace plastic materials in the future.
„One example of an application is moving boxes, which can be exposed to rain for longer periods without softening thanks to our hydrophobic layers. Our aim is to reduce dependence on fossil resources and support the transition to a resource-efficient economy.“
Martin Bellmann
Source: Fraunhofer IST